What is Lung Cancer?
- Lung cancer begins in the lungs and may spread to lymph nodes or other organs in the body, such as the brain.
- Lung cancer is one of the most common type of cancers and is the leading cause of cancer-related death among both men and women
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is classified according to the size of the cell. The two major forms of lung cancer are:
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) comprises approximately 85% of all lung cancers. When the cancer cells are not small, the cancer is known as non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Different subtypes of these cancers are found- adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) If the cells are small the cancer is known as small cell lung cancer (NCLC) and makes approximately 10 to 20% of all lung cancers. This cancer grows quickly, and shows a positive response to chemotherapy and radiation therapy as a result. Unfortunately, for most people, this cancer will return at some point.
What are the Causes for Lung Cancer and the Risk Factors?
-
Smoking is the main risk factor for lung cancer. But anything that makes contact with the lungs and increases the chance of getting lung cancer is a risk factor.
-
Smoking tobacco in cigarettes, cigars or pipes is responsible for 87% of lung cancer cases in the United States. The more years you smoke and in greater quantity, the higher your risk of lung cancer.
-
Exposure to secondhand smoke
-
If you stop smoking, your risk of lung cancer becomes lower as time goes by.
-
If you smoke and have other risk factors, your chance of getting lung cancer is higher.
-
Other risk factors and causes for lung cancer include:
-
Family history of lung cancer
-
Previous lung cancer
-
Radiation therapy to the breast or chest
-
Air pollution
-
Inherited and acquired gene mutations
-
Lung diseases such as tuberculosis (TB)
-
Rubber production and crystalline silica dust
-
Products of combustion (burning coal, incomplete combustion, coal gasification, soot, diesel engine exhaust)
-
Toxic gases
-
Exposure to certain chemical substances and materials such as asbestos, nickel, silica, radiation, arsenic, radon, chromium, nickel, soot, or tar
-
Exposure to radon gas
-
Ionizing radiations
Not everyone with these risk factors develops lung cancer. However, if you believe to be at risk, it is advised to call our office today for a consultation.
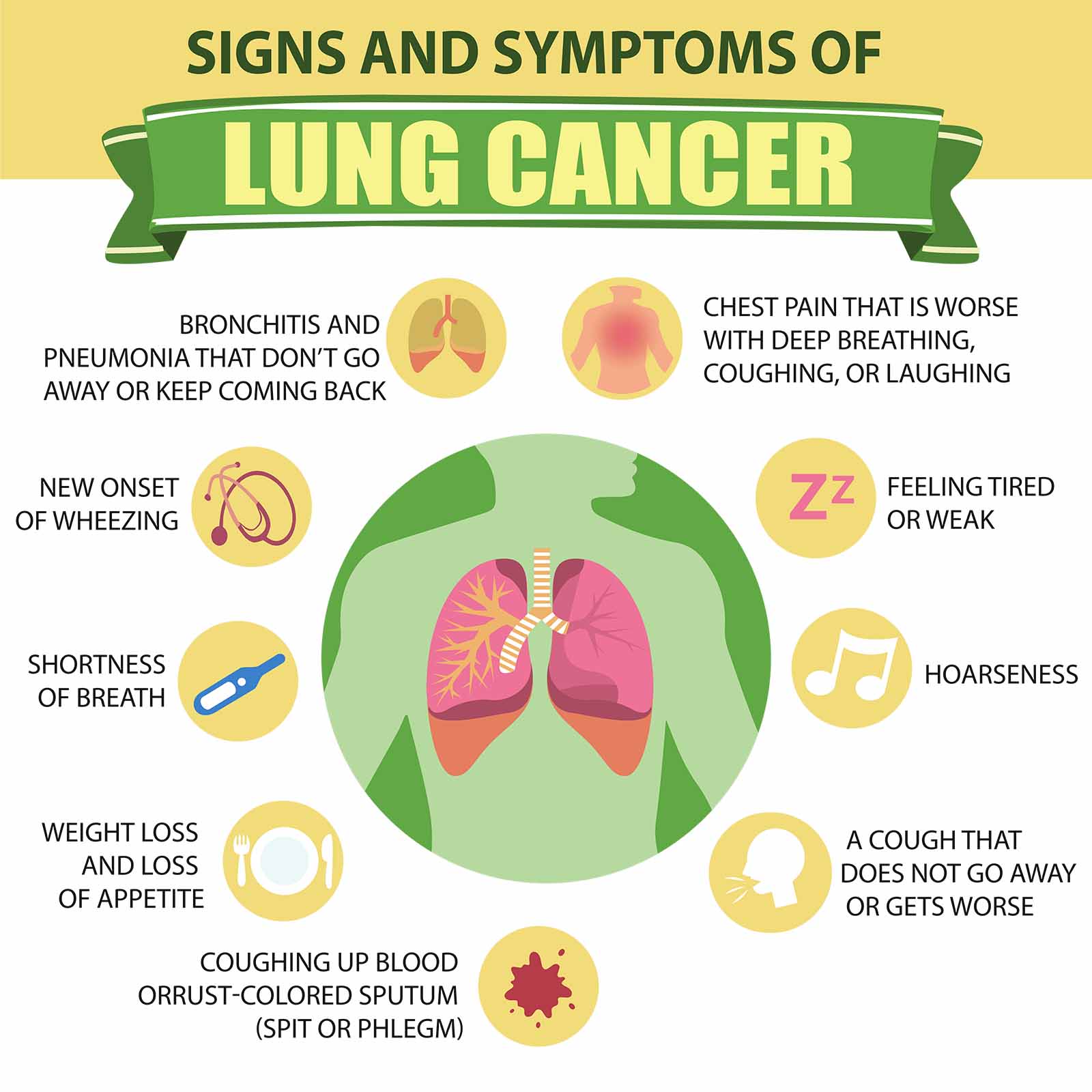
What are the Symptoms of Lung Cancer?
In most instances, lung cancers do not have any symptoms. Lung cancer symptoms vary from person to person. Symptoms may not be evident until the lung disease is in its severe stage. Symptoms may include:
- Coughing getting worse over time and not disappearing
- Short Breath
- Chest pain, back pain, and shoulder pain
- Loss of appetite
- Weakness
- Wheezing
- Difficulty with swallowing
- Coughing up blood
- Voice change or being hoarse
- Feeling tired
- Clubbing of fingernails (unusual rounded appearance)
- Repeated lung diseases such as pneumonia or bronchitis
- Persistent and intense coughing
- Weight loss
If lung cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it may cause:
- Bone pain
- Weakness and numbness in the arms and legs
- Headache, dizziness or seizure
- Jaundice (yellow coloring) of skin and eyes
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck or shoulder
Contact your oncologist if you believe you may be at risk and/or are experiencing some of the symptoms listed above. Your oncologist will determine your best course of treatment that is best suited for you.
Q & A
A: Yes, exposure to smoke is a risk factor for cancer by itself.
A: For those who stop smoking, there is still a risk for cancer but it does decrease over time after quitting.
A: Yes, air pollution is linked with lung cancer as a risk factor.
How Is Lung Cancer Treated?
Lung cancer is treated in several ways, which depends on the type of lung cancer and its staging. People with non-small cell lung cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments. People with small cell lung cancer are usually treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
- Surgery: People suffering from early-stage cancer will usually undergo surgery to remove the tumor. There are three important types of lung cancer surgeries-
- Lobectomy: An affected lobe of the lung is removed
- Pneumonectomy: Here, a lung is removed
- Wedge Resection:A segment of the affected lung is removed
- Radiotherapy: During the initial stage of lung cancer, it is used to eliminate cancer cells completely. In advanced stages, it aims to slow down the progress of cancer and lessen its symptoms.
- Chemotherapy: Uses special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer cells. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins, or sometimes both.
- Targeted Drug Therapy: Interferes with the ways cancer cells function
The majority of lung cancer patients are diagnosed with advanced disease. For these patients, conventional treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation are unlikely to result in complete cures, although they may significantly improve survival and provide symptom relief.
Odds of survival can greatly improve for people with the most common type of lung cancer if they are given a new drug that activates the immune system along with chemotherapy.
How To Prevent Lung Cancer?
- Stay away from smoking
- Keep away from passive smoking, i.e. stay away from others who smoke. Exposure to smoke is a risk factor for cancer by itself.
- Check your home for radon if you happen to reside at a place where radon is a problem
- Protect yourself from inhaling toxic gases
- Avoid harmful chemical substances
- Eat a healthy balanced diet
- Exercise regularly
At HEMATOLOGY & ONCOLOGY CARE we customize your Lung Cancer care so you can receive the most advanced, least invasive treatment with the fewest side effects. Planning of the treatment involves an interdisciplinary team of medical professionals. This usually implies a meeting of different specialists we have at HOC, called a multidisciplinary opinion. In this meeting, the planning of treatment will be discussed based on the relevant information summarized above.