What is Lymphoma?
Lymphoma refers to cancers of the lymphatic system (the system that produces, stores, and carries white blood cells that fight infections), and the two main types of lymphoma are:
- Hodgkin lymphoma, which spreads in an orderly manner from one group of lymph nodes to another. Hodgkin lymphoma can often be cured.
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which spreads through the lymphatic system in a non-orderly manner.
Both Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma are present in children, teens, and adults.
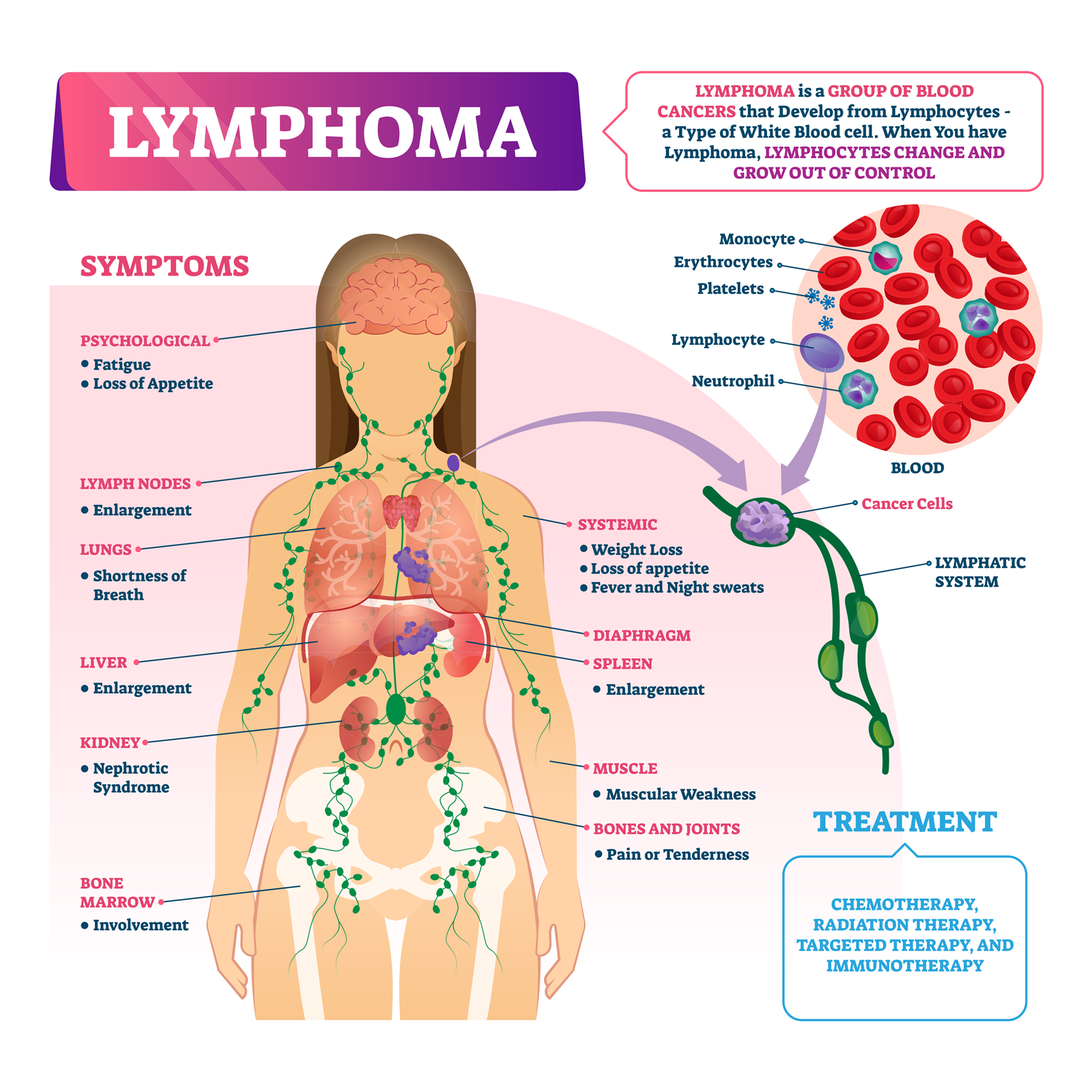
What are the Symptoms of Lymphoma?
Symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma include:
-
Swollen lymph nodes, especially in the part of the body where the lymphoma starts to grow such as the swoles on the groin, armpits, or neck.
-
Fever
-
Unintended weight loss
-
Fatigue or tiredness
-
Night sweats
Contact our office today if you believe you may be at risk and/or are experiencing some of the symptoms listed above. Our team of doctors will determine the course of treatment that is best suited for you.


What are the Risk Factors and Causes of Lymphoma?
The different types of Lymphoma have different risk factors and causes.
Risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma include:
-
The Epstein-Barr virus (often called mono) is associated with the development of Hodgkin lymphoma.
-
Weakened Immune Systems: People infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) have increased the probability of developing Hodgkin lymphoma. People who take medicines to suppress the immune system are also at higher risk.
-
Family History is found to be a link in some cases but not many.
-
Gender: occurs slightly more often in males than in females.
-
Age: most common in early adulthood (especially in a person’s 20s) and in late adulthood (after age 55)
Risk factors for Non-Hodgkin lymphoma include:
-
Age: Most cases occur in people in their 60s or older.
-
Family history: Having a first degree relative with Non-hodgkin lymphoma increases the risk of developing it.
-
Exposure to Certain Chemicals and Medications such as benzene and certain herbicides and insecticides
-
Radiation exposure
-
A weakened immune system
-
Infection: Infection with human T-cell lymphotropic virus, Epstein-Barr virus, herpes virus 8, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are linked to lymphoma risk.
Q & A
A common symptom of lymphoma is for it to cause lymph nodes to swell, resulting in a lump or lumps usually on the neck, armpit, or groin.
A: A common symptom of lymphoma is for it to cause lymph nodes to swell, resulting in a lump or lumps usually on the neck, armpit, or groin.
A: Having infectious mono does not mean you have a lymphoma, you should contact your PCP to get your spleen and lymph nodes evaluated for further testing
What are the Treatments for Lymphoma?
At HEMATOLOGY & ONCOLOGY CARE we customize your Lymphoma care so you can receive the most advanced, least invasive treatment with the fewest side effects. Planning of the treatment involves an interdisciplinary team of medical professionals. This usually implies a meeting of different specialists we have at HOC, called a multidisciplinary opinion. In this meeting, the planning of treatment will be discussed based on the relevant information summarized above.
There are four major types of lymphoma treatments available, namely
Chemotherapy: Uses special medications that are meant to shrink or kill the cancer cells. These drugs can be oral pills or given to you in I.V. depending on your specialized treatment plan.
Radiotherapy: Using high-energy rays (similar to X-rays) to kill the cancer cells.
Stem cell or Bone marrow transplant uses a high dosage of radiation or chemotherapy to specifically kill targeted cancer cells.
Antibody therapy/targeted therapy causes the immune system to target and attack the cancer cells.